Use sales competencies for assessment, selection, and development.
Make assessment, selection, and development easier. Use a sales competence model to inspire improvement and performance. Have us create your sales competencies model. Take a shortcut. Call us now or schedule a Zoom call to discuss suitability.
How does a sales competency model help?
Sales competencies provide a framework and benchmark for the appraisal and development of existing staff and assessing new hire candidates.
Many benefits are available to those who make competence models a central pillar of their business. Appraisals become more transparent, balanced, and fair. Selection can be based on verifiable knowledge, abilities, and habits. And staff can be expected to take the initiative for their own development. Better management, lower staff turnover, and more motivated people all contribute to increased sales and profits.
What is a Sales Competency Framework?
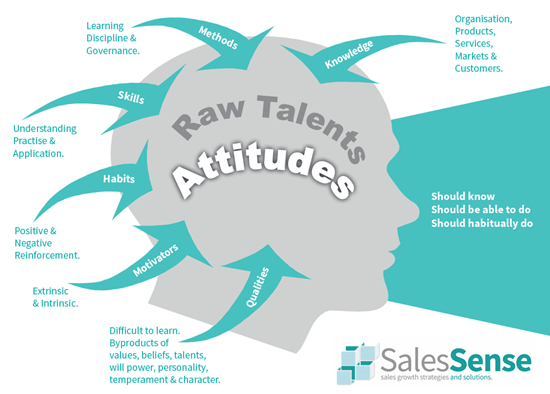
Sometimes referred to as a sales competency matrix, a framework is a list of things salespeople should know, be able to do, and do habitually in their work. The knowledge is specific to the sales environment that salespeople are working in, however, each thing that needs to be known can have a general label. For example, how the main product they are selling came into being. Capabilities are more straightforward. Habits might be labelled daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, and annual actions.
What are Examples of Sales Competencies?
You can use the nineteen sales competencies summarised below as a base for developing your own sales competence model.
Take a shortcut. Have us do the work for you. We have done it before, so we can help you complete your model faster. Call us now or schedule a Zoom call and explore the potential.
Learn more about modelling sales competencies.
The Nineteen Sales Competence Factors
1. Answering Common Customer Questions
There are six common questions that buyers have in mind when considering new purchases or suppliers. Those who have good answers increase credibility, reduce anxiety, and develop trust more easily.
See the questions here.
Schedule a call to test your answers here.
2. Market and Industry Understanding
Salespeople who have expert knowledge of the market and industry that they operate in, find it easier to build important contacts and recognise worthwhile opportunities. It helps them establish credibility, communicate value, and develop trust.
3. Customer and Prospect Understanding
The ability to persuade depends on understanding. Knowing how a customer’s business works, helps salespeople position the value they offer and acquire trusted advisor status.
4. Company Understanding
Those who know their company's goals, objectives, strategy, needs, strengths, and weaknesses understand the capabilities and resources available to address the market.
Test sales knowledge with our free assessment.
Have us prepare onboarding and learning materials for your markets, customers, sales prospects, and company. Learn more.
5. Written Communication
In addition to general customer communications via letter and email, many salespeople must prepare their own quotations and proposals. The increasingly important personal marketing and digital selling techniques rely heavily on writing skills.
6. Understanding and Articulation of Value
A complete understanding of the value provided by the products or services represented is an aspect of a salesperson's knowledge that shouldn't be taken for granted. Equally important is the ability to communicate the value effectively.
Test sales knowledge with our free assessment.
7. Proactive Prospecting
If marketing activities don’t generate enough leads and enquiries, salespeople must be able to find their own. Effective and efficient prospecting can make all the difference when business is hard to come by.
Get the latest training: Sales Prospecting for BDMs and Top SDR
Try a single one-hour session to assess the value.
8. Networking for New Opportunities
Networking is an alternative means of finding new prospects. It depends on having a favourable relationship with a wide range of business contacts in the industry and related industries.
Arrange a virtual workshop on networking for new business opportunities. Learn more or arrange a call to discuss the content.
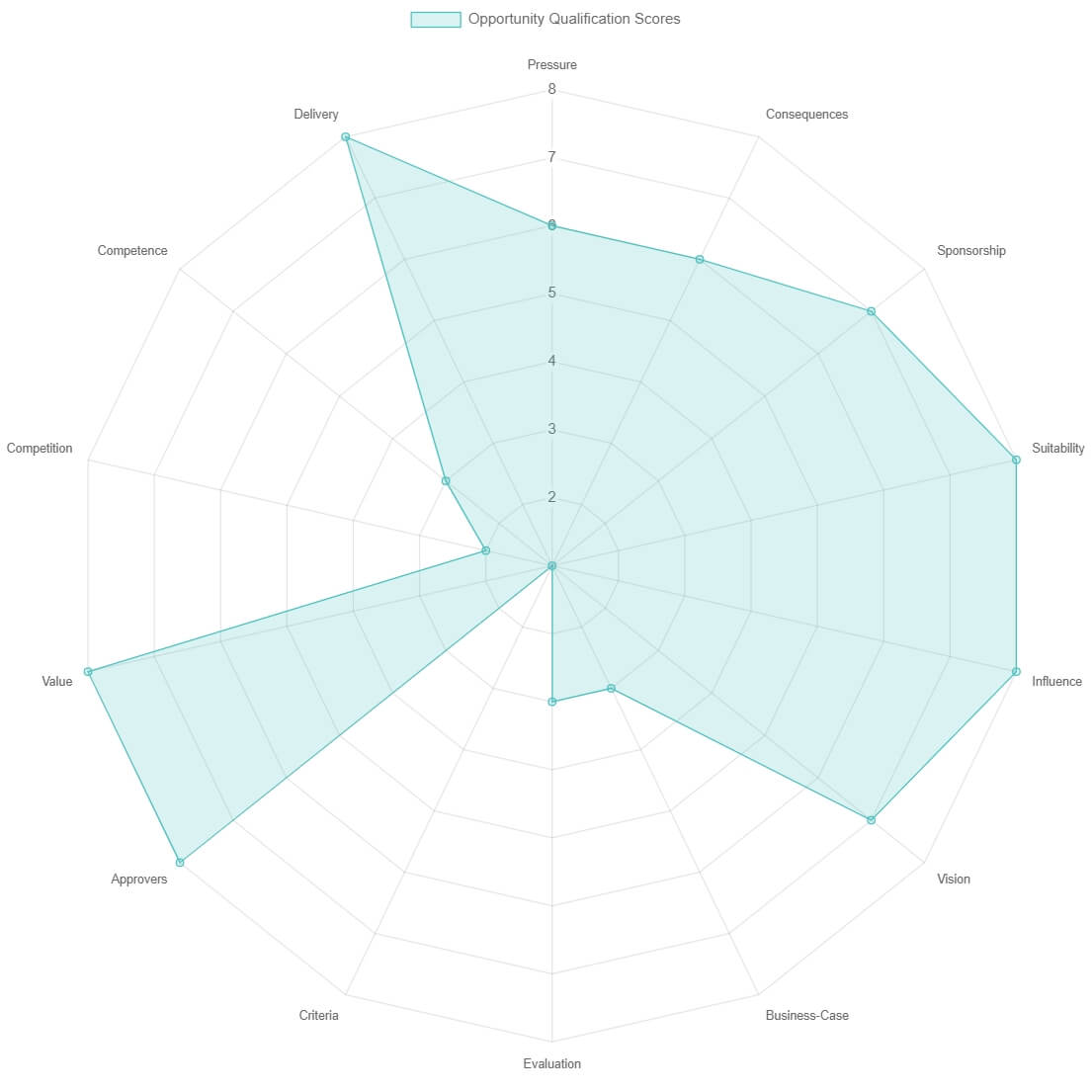
9. Opportunity Qualification
Doing things right is a waste of time if people don’t first choose the right things to do. Sales qualification has a substantial impact on success.
There are 15 quantifiable enquiries that score the likelihood of winning any B2B sale. Do you know what they are? Are you using them to eliminate the guesswork?
Try our free Sales Win Predictor.
10. Forecast Accuracy
Apart from an accurate forecast being essential for good business management, it also helps salespeople secure the right resources to win the business opportunities addressed.
Four distinct reporting pillars underpin an accurate sales forecast.
They are the sales stage, the sales stage conversion rate, quantified qualification, and the salesperson's confidence.
Learn how to use the four pillars in a one-hour one-to-one call or group workshop.
11. Organisation and Time Management
Forethought, planning, and preparation precede success. Making good use of the time available and paying attention to detail are important aspects of sales competence.
Take a one-to-one coaching programme to develop better organisation and time management habits.
12. Managing the Sales Process
Using a system or method that has proved effective elsewhere provides a benchmark for measuring progress and a common language for communicating internally. Frameworks and checklists help sellers avoid mistakes and develop better methods.
Learn more about sales process improvement.
13. Interpersonal Communication
Good communication is a foundation stone of success. Many aspects of sales competency depend on the salesperson’s ability to discover information that isn't publicly available, shift another person's perspective, and make a convincing presentation.
Take our Persuasive Interpersonal Communication course.
14. Handling Objections
Buying objections thrown up by customers can delay or stall business that otherwise could be concluded. Salespeople need the ability to turn objections around.
Improve objection handling with a one-hour virtual workshop.
15. Progressing a Sale
Moving a sale forward depends on the ability to manage the customer's buying process. Does your sales process complement the typical buying process used by your customers?
Do you need to learn how to control a customer's buying process?
16. Negotiating Terms
Some elements of negotiation are important throughout a sale however the final negotiation often brings out different behaviours, tactics, and ploys. Salespeople need to be able to negotiate win/win outcomes.
Take our sales negotiation skills training via a series of virtual workshops or through an in-house course.
17. Self-Development
In a competitive market, organisations must continuously increase productivity. Salespeople must keep getting better. Otherwise, their company will inevitably be overtaken by competitors.
Accelerate self-development through a one-to-one coaching programme.
Use our free sales exam assessments to guide development.
Take our Build a Professional Sales Career course.
18. Sales Mindset
Attitude dictates thinking and thinking dictates speech and actions. There are attitudes that help salespeople succeed and there are those that hinder them. While attitude itself cannot be a competency, having attitudes compatible with success, can be considered an aspect of sales competence.
"Altitude is a function of attitude rather than aptitude." Anonymous
Arrange a call to discuss useful sales attitudes.
19. Sales Motivators
Motivation has a major impact on the attitudes that salespeople nurture, the decisions they take, and the actions that follow. Consequently, a salesperson's intrinsic motivators, have a bearing on success which differs according to the role being fulfilled.
Take our free Sales Motivation Assessment.
Explore individual differences and motivations in a one-hour workshop.
If you need ways to measure sales competencies or want to create a sales competence model for training or assessment, we can help. Telephone +44 (0)1392 851500. Alternatively, use the contact form here or send an email to custserv@salessense.co.uk.